Hyperkalemia: Causes, Risks, and How Medications Can Trigger It
When your blood has too much hyperkalemia, a condition where potassium levels in the blood rise above normal limits. Also known as high potassium, it’s not just a lab number—it can quietly mess with your heart rhythm and even stop your heart if ignored. Most people don’t feel it until something serious happens, which is why understanding what causes it matters more than you think.
One of the biggest triggers is kidney disease, when kidneys lose their ability to filter excess potassium from the blood. But it’s not just about failing kidneys. Common medications like ACE inhibitors, drugs used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure, can block the body’s natural way of getting rid of potassium. Same goes for potassium-sparing diuretics, a type of water pill that stops your body from losing potassium. People taking these meds—especially older adults or those with diabetes—are at higher risk, often without knowing it.
Other factors like severe injuries, uncontrolled diabetes, or even too many potassium supplements can push levels up. The scary part? Symptoms are vague—muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, nausea—and often get mistaken for something else. That’s why regular blood tests are critical if you’re on long-term meds for blood pressure or heart conditions.
The posts below dig into real-world cases and drug interactions that can lead to hyperkalemia. You’ll find guides on how certain medications affect potassium, what to ask your doctor, and how to spot early warning signs before it turns dangerous. No fluff. Just clear, practical info to help you stay safe while managing your health.
Valsartan-Hydrochlorothiazide and Potassium: What You Need to Know
Learn how Valsartan-Hydrochlorothiazide affects potassium, signs of low or high levels, monitoring tips, diet advice, and when to seek medical help.
About
Medications
Latest Posts


Supporting a Loved One with OCD: Practical Tips for Family and Friends
By Orion Kingsworth Sep 22, 2025
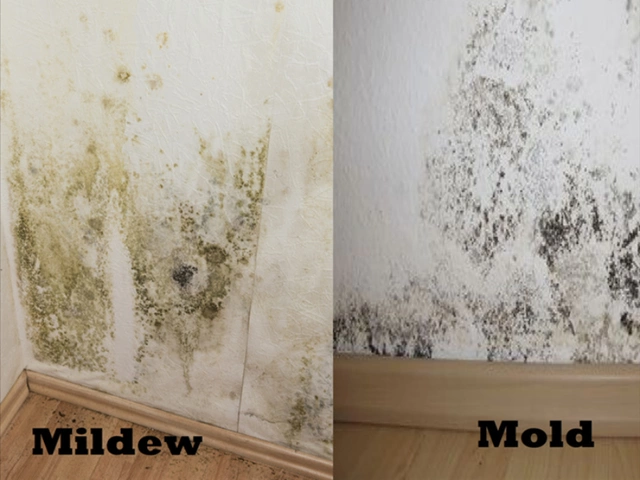

Itraconazole and its use in combating mold and mildew in homes
By Orion Kingsworth May 13, 2023

Generic Appearance Changes: Why Your Pill Color and Shape Keep Changing
By Orion Kingsworth Jan 19, 2026