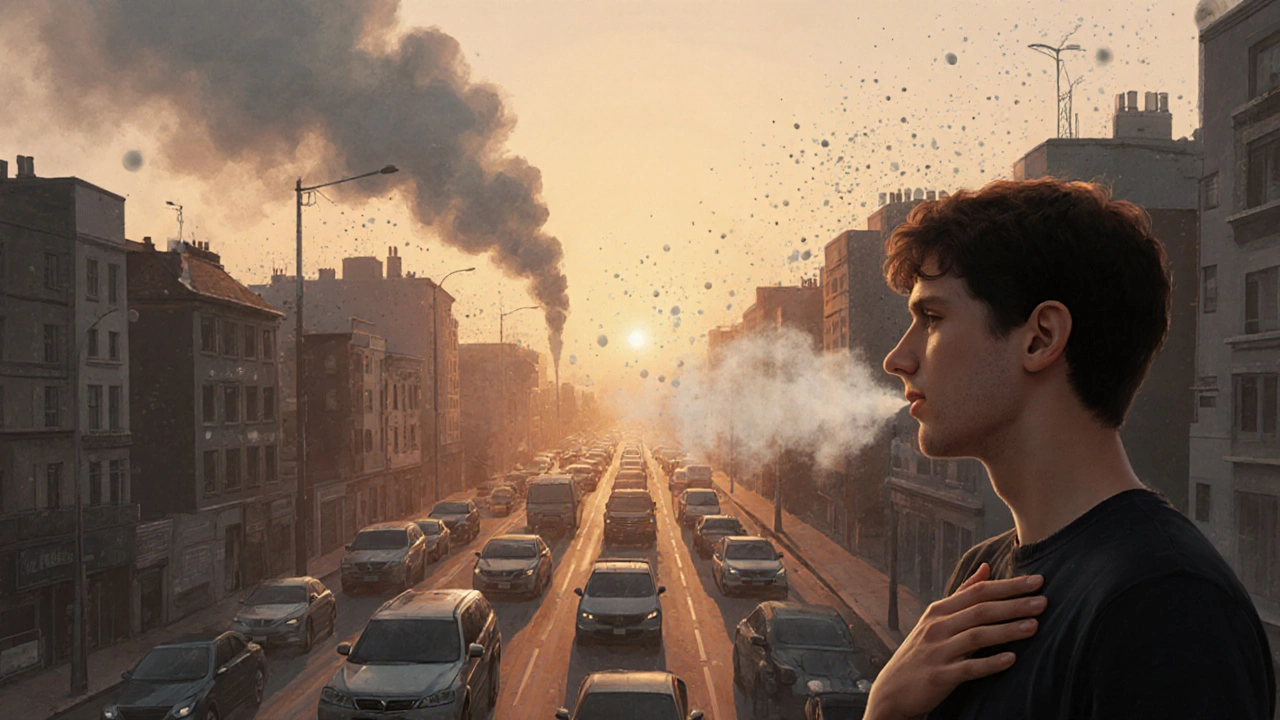
Air Pollution and Asthma: How Clean Air Affects Your Breathing
When you breathe in air pollution, a mix of harmful gases and particles in the atmosphere that irritate the lungs and worsen respiratory conditions. Also known as outdoor air contamination, it doesn’t just make your eyes water—it can turn a mild asthma cough into a full-blown attack. If you or someone you know has asthma, dirty air isn’t just uncomfortable—it’s dangerous. Studies show that even short-term spikes in ozone, PM2.5, or nitrogen dioxide can send thousands to the ER each year. This isn’t theoretical. In cities with heavy traffic or industrial zones, asthma hospitalizations rise sharply during smog alerts. You don’t need a degree in environmental science to understand this: if the air smells bad or looks hazy, your lungs are paying the price.
asthma triggers, specific substances or conditions that cause airway narrowing and breathing difficulty in people with asthma. Also known as asthma exacerbators, it includes more than just pollen or pet dander. air quality and health, the direct relationship between the cleanliness of the air you breathe and your respiratory function is one of the most powerful, yet ignored, factors in managing asthma. Unlike allergens you can avoid at home, pollution follows you everywhere—on your commute, at the park, even indoors if windows are open. It doesn’t matter if you take your inhaler daily; if you’re constantly exposed to vehicle exhaust or factory smoke, your lungs stay inflamed. And kids? They’re even more vulnerable. Their lungs are still growing, and they breathe faster, pulling in more polluted air per pound of body weight.
What’s in the air that makes asthma worse? air pollution asthma isn’t just one thing. It’s diesel fumes from trucks, fine dust from construction sites, smoke from wildfires, and ground-level ozone formed when sunlight hits car emissions. These aren’t just environmental issues—they’re medical ones. The same pollutants that turn skies gray also make inhalers less effective over time. You might think your medication is failing, but it’s the air around you that’s changing the game. And while you can’t control the weather or the factory down the road, you can learn how to reduce your exposure. Check local air quality reports. Avoid outdoor exercise during peak traffic hours. Use air filters indoors. These aren’t just tips—they’re survival tools for anyone with asthma.
The posts below give you real, no-fluff guidance on how pollution affects asthma, what the science says, and how to protect yourself every day. You’ll find practical steps to reduce exposure, understand warning signs before an attack, and recognize which environmental factors are most dangerous in your area. No theory. No jargon. Just what works.
How Environmental Factors Influence Bronchial Asthma
Explore how air pollution, pollen, dust mites, smoke, humidity and more influence bronchial asthma, and learn practical steps to reduce exposure for better breathing.
About
Health and Medicine
Latest Posts

Medication Safety in Kidney Disease: How to Dose Drugs Correctly and Avoid Nephrotoxins
By Orion Kingsworth Jan 4, 2026

Buy Cheap Generic Crestor Online - 2025 Guide to Safe Savings
By Orion Kingsworth Oct 8, 2025

Osteoarthritis of the Hip: How Weight Loss Can Preserve Your Joint and Reduce Pain
By Orion Kingsworth Nov 17, 2025

