Ziprasidone: What It Is, How It Works, and What You Need to Know
When doctors prescribe Ziprasidone, a second-generation antipsychotic medication used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Also known as Geodon, it helps calm overactive brain signals that cause hallucinations, delusions, and extreme mood swings. Unlike older antipsychotics, Ziprasidone doesn’t always cause heavy sedation or weight gain—but it’s not without risks. It affects dopamine and serotonin, two key brain chemicals tied to mood and perception. This dual action makes it useful when other drugs fail, but it also means you need to watch for side effects like dizziness, nausea, or changes in heart rhythm.
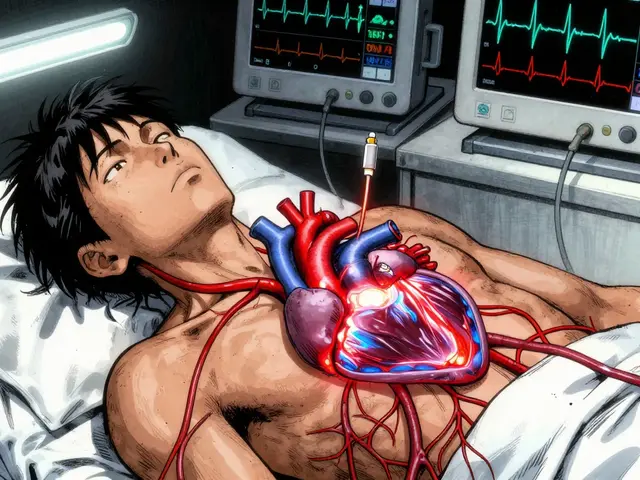
People taking Ziprasidone, a second-generation antipsychotic medication used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Also known as Geodon, it helps calm overactive brain signals that cause hallucinations, delusions, and extreme mood swings. often combine it with therapy or lifestyle changes. It’s not a quick fix. Most users notice improvements in thinking and mood after 2–4 weeks, but full effects can take months. If you’re on Ziprasidone, your doctor will likely monitor your ECG, because it can slightly prolong the QT interval—a heart rhythm marker. That’s why it’s not usually the first choice for people with existing heart conditions. It’s also taken with food; skipping meals can drop absorption by half. This isn’t a drug you can just stop. Tapering off under medical supervision prevents withdrawal symptoms like rebound psychosis or anxiety spikes.
Ziprasidone doesn’t work the same for everyone. Some people tolerate it well and get back to normal life. Others switch after a few months due to side effects like restlessness, muscle stiffness, or fatigue. It’s often compared to olanzapine, a common antipsychotic used for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, known for weight gain but strong efficacy or risperidone, a widely used antipsychotic for psychosis and irritability, with more movement-related side effects. Each has trade-offs. Ziprasidone’s edge? Less weight gain than olanzapine, fewer sedative effects than risperidone. But if you have a history of heart issues, your doctor might pick something else.
What you’ll find below are real, practical posts from people who’ve lived with these choices. You’ll see how Ziprasidone fits into daily routines, what side effects actually feel like, how it stacks up against other meds, and what to watch for when starting or switching. No fluff. No theory. Just what works—and what doesn’t—for real patients managing serious mental health conditions.
Geodon (Ziprasidone) vs. Alternatives: A Detailed Comparison
A comprehensive comparison of Geodon (ziprasidone) with common antipsychotic alternatives, covering efficacy, side effects, cost, and practical decision factors.
About
Medications
Latest Posts

Why Prescription Drug Prices Are So High in the United States: The Real Reasons Explained
By Orion Kingsworth Feb 6, 2026

Preventive Measures for Building Resilient Pharmaceutical Supply Chains to Prevent Drug Shortages
By Orion Kingsworth Dec 23, 2025

How to Update Your Allergy List Across All Healthcare Providers
By Orion Kingsworth Nov 14, 2025

